Companies of all sizes seek ways to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and maintain a competitive edge. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become a cornerstone for achieving these goals. But what is ERP, and how can it benefit UK businesses? This comprehensive guide will explore the fundamentals of ERP, its key features, benefits, and how it can be a game-changer for your organisation.
What is ERP (enterprise resource planning)?
ERP refers to a software system that integrates and centralises various core business processes and data into one unified platform. These processes typically include finance, human resources, supply chain management, customer relationship management, manufacturing, and more. By storing all relevant information in a single database, ERP provides real-time insights and enables seamless communication between different departments, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
ERP software is widely adopted across businesses of all sizes in the UK, considered essential for large enterprises, and increasingly utilised by small businesses as they grow. Given the complexities of the global economy and modern consumer demands, there is a critical need to streamline business processes and effectively manage and optimize data. ERP systems typically serve as the backbone for achieving these essential capabilities, tailored to meet the specific needs and regulations of the UK market.
Understanding ERP: The Basics
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a type of software utilised by organisations to manage daily business activities, including accounting, procurement, project management, risk management and compliance, and supply chain operations. ERP systems integrate a wide range of business processes, facilitating seamless data flow. By consolidating an organisation’s shared transactional data from multiple sources, ERP systems eliminate data duplication and ensure data integrity with a single source of truth.
For UK businesses, the importance of ERP systems cannot be overstated. ERP systems enhance efficiency and accuracy in a competitive market, enabling companies to make informed decisions quickly. They support compliance with UK regulations, streamline operations, and improve productivity. By providing real-time insights and fostering better collaboration, ERP systems help UK businesses stay agile and responsive to market changes, ultimately driving growth and success.
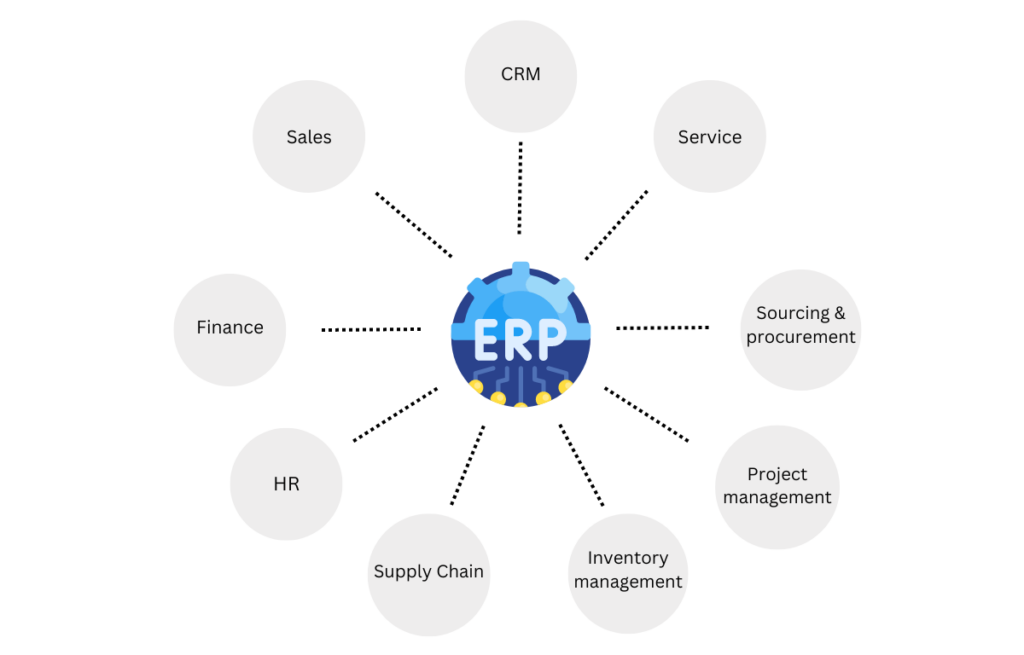
Key components of an ERP system
An ERP system comprises software components, known as modules, each dedicated to specific business processes. Some modules are universally essential across various industries and are prioritised for initial deployment:
Finance: The ERP finance module automates fundamental tasks such as accounting, invoicing, financial analysis, forecasting, and reporting. This module frequently drives companies to transition from standalone accounting software to ERP systems. As business complexity increases, the necessity becomes clear for a unified system to handle all financial transactions and accounting across multiple business units and product lines.
Human resources (HR): Human resources is another essential process companies aim to enhance through ERP systems. Basic HR functionalities include managing employee records, benefits, and payroll, while advanced systems also incorporate talent management features such as recruitment and performance management.
Supply Chain Management (SCM): Manufacturing or distribution companies commonly integrate a supply chain management (SCM) module to monitor inventory levels and oversee warehouse and transportation operations throughout the supply chain. For more intricate business requirements, they may incorporate separate warehouse management systems (WMS) and transportation management systems (TMS) from different software providers to efficiently manage these logistics functions.
Sales and marketing: The sales module manages communications with prospects and customers, leveraging data-driven insights to boost sales and target leads effectively with the right promotions and upsell opportunities. It encompasses the entire order-to-cash process, including order management, contract management, billing, sales performance management, and sales force support. This module ensures streamlined operations, enhances customer interactions, and optimises sales strategies.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Manages interactions with customers and prospects. It includes functionalities for sales force automation, marketing automation, customer service, and support.
Inventory Management: Inventory management tracks inventory levels, manages stock, and optimizes warehouse operations. It includes functionalities for order fulfillment, stock movements, and inventory valuation, ensuring efficient inventory control and reducing costs.
Procurement: The procurement module manages the process of acquiring goods and services. It includes vendor management, purchase orders, contract management, and procurement analytics, enabling organizations to streamline procurement processes and manage supplier relationships effectively.
Service Management: Service management handles service operations, including service contracts, warranties, service orders, and field service management. It helps improve customer service and manage service delivery efficiently, ensuring high levels of customer satisfaction.
Project Management: Project management supports planning, execution, and monitoring of projects. Key features include project budgeting, resource allocation, task management, and project reporting, enabling organizations to manage projects efficiently and achieve their goals on time and within budget.
These are just a few key components of an ERP system. Depending on your chosen ERP software, there may be additional modules and functionalities tailored to meet the specific needs of your business.
Read more: What is the Difference between ERP & CRM Software?
Key Features of ERP Systems
ERP systems are designed to integrate various business processes into a unified system. Here are some of the key features:
- Centralised Database: One of the most critical features of an ERP system is a centralised database that ensures data consistency and accuracy across the organisation.
- Automated Processes: ERP systems automate routine tasks and business processes, reducing manual intervention and increasing efficiency.
- Real-Time Data: With real-time data access, businesses can make informed decisions quickly, improving responsiveness and agility.
- Scalability: ERP systems are scalable, allowing businesses to add new users, departments, and functionalities as they grow.
- Customisation: Modern ERP systems offer customisable modules that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different industries and business models.
Benefits of ERP for UK Businesses
Implementing an ERP system can offer numerous benefits to UK businesses. As companies grow and face increasing complexities, integrating an ERP system becomes crucial for maintaining competitiveness and efficiency. By facilitating easier data sharing across modules compared to separate systems, ERP simplifies the management of cross-departmental business processes. ERP systems enable deeper insights through real-time data and business intelligence, leveraging advanced technologies like advanced analytics, artificial intelligence (including machine learning), and the industrial internet of things (IIoT) that are increasingly integrated into many ERP platforms.
1. Improved Efficiency and Productivity
One of the greatest advantages of ERP is its ability to streamline business processes. By automating routine tasks and minimising manual data entry, ERP reduces the risk of errors and improves productivity. For instance, instead of maintaining separate sales, inventory, and order tracking systems, an ERP system can integrate these processes, allowing for smoother operations and better decision-making.
2. Enhanced Visibility and Reporting
ERP systems provide comprehensive visibility into every aspect of your business. With real-time access to data, you can generate accurate reports, analyse key performance indicators, and gain valuable insights. This empowers decision-makers to make informed choices, identify trends, and allocate resources efficiently, leading to better strategic planning and growth opportunities.
3. Improved Collaboration
ERP systems foster collaboration by providing a single platform where employees can access and share information. This breaks down silos and ensures that everyone is on the same page, enhancing teamwork and communication.
4. Cost Savings
Implementing an ERP system can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. By eliminating manual processes, reducing duplication of effort, and optimising resource allocation, businesses can achieve higher operational efficiency, ultimately saving time and money. Additionally, ERP can help minimise inventory carrying costs, prevent stockouts, and optimise supply chain operations, resulting in improved profitability and customer satisfaction.
5. Scalability and Adaptability
As businesses in the UK grow and expand, ERP systems offer scalability and adaptability. Whether you acquire new branches, expand into international markets, or introduce new product lines, ERP can accommodate these changes smoothly. It can easily handle increased transaction volumes, support multiple currencies, and adapt to changing regulatory requirements, ensuring your business remains efficient and compliant.
6. Regulatory Compliance
For UK businesses, adhering to regulatory standards is crucial. ERP systems help ensure compliance with industry regulations by providing tools for tracking and reporting necessary data. By integrating ERP, businesses can stay GDPR compliant and meet other regulatory requirements efficiently. For more detailed insights on how ERP systems aid in compliance, check out our blog Staying Compliant in the UK.

Read more: ERP examples in different industries
Types of ERP systems
ERP products typically differ based on the company size they target, the computing infrastructure they support, and whether they include industry-specific features.
In the small business sector, certain vendors offer entry-level ERP systems. These solutions often include essential modules such as HR, finance, order management, and CRM. They are designed to be relatively straightforward to implement, catering to the needs of smaller organisations.
Certain vendors offering entry-level ERP cater to small and midmarket businesses (SMBs) and assert that their products can scale effectively to accommodate business growth.
Large enterprises, which typically generate over $1 billion in revenue and employ thousands of staff, usually require large ERP systems known by their extensive modules, enhanced capabilities within each module, and the ability to support thousands, or even hundreds of thousands, of users.
Read more: Why Enterprise Companies Choose Dynamics 365 for Digital Transformation
Types of ERP deployment
On-premises, cloud, and hybrid ERP deployment options have evolved significantly since ERP systems were first introduced in the 1970s. Initially, ERP systems ran exclusively on premises hosted on the company’s own computers. Today, ERP systems are just as likely to operate in the cloud, hosted and maintained by the vendor or a service provider, allowing users to access the software via the internet from desktop or mobile devices. Hybrid ERP solutions combine both on-premises and cloud-based modules.
These different deployment models significantly impact the capabilities, user experience, cost, implementation speed, and target market of an ERP product.
On-premises ERP
On-premises ERP systems typically require a significant upfront investment involving the purchase of software licenses for a specified number of users. These implementations often have lengthy timelines, sometimes extending over several years, and upgrades to new versions can be slow. However, on-premises ERP systems offer two major advantages over many cloud-based ERP solutions: they can be extensively customised to meet specific business requirements and are generally easier to integrate with other critical on-premises systems, such as factory automation or warehouse management systems.
Additionally, organisations in highly regulated industries or government sectors may have strict data residency requirements that necessitate keeping their systems and data on-premises.
Cloud ERP
Software-as-a-service (SaaS)
With SaaS ERP, the software operates on a network of remote servers rather than within a company’s server room. The cloud provider handles patching, managing, and updating the software multiple times a year, contrasting with the costly and infrequent upgrades (every 5 to 10 years) typical of on-premises systems. This model can significantly reduce operational and capital expenses by eliminating the need for companies to purchase software and hardware or hire additional IT staff. Consequently, resources can be redirected towards new business opportunities, ensuring the organisation always has the most recent ERP software. Employees can then shift their focus from IT management to more value-added tasks like innovation and growth.
Read more: 7 Ways Cloud ERP Helps You Reduce Risk
Hybrid ERP
The hybrid cloud ERP model offers an ideal solution for companies seeking a blend of both on-premises and cloud solutions to meet their business requirements. In this model, certain ERP applications and data are hosted in the cloud while others remain on-premises. This approach is often referred to as two-tier ERP, providing the flexibility to leverage the strengths of both deployment methods.
Popular ERP Vendors for UK Businesses
The UK market boasts a wide array of ERP vendors, offering both on-premises and cloud options to cater to diverse business needs. When selecting an ERP system, UK businesses should consider their specific industry requirements, company size, and long-term growth plans.
Among the many solutions available, several ERP systems stand out for their unique features and widespread adoption:
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: Known for its flexibility and integration capabilities, Dynamics 365 is ideal for businesses of all sizes. It offers a unified platform integrating CRM and ERP functionalities, enabling seamless operations across various departments. Its modular design allows businesses to start with what they need and scale up as they grow.
- SAP Business One: Tailored for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), SAP Business One provides robust functionalities and scalability. It covers key areas such as financials, sales, customer relationship management, inventory, and operations. SAP Business One’s comprehensive features make it an excellent choice for growing businesses seeking to streamline their operations.
- Oracle NetSuite: This cloud-based ERP solution offers comprehensive business management capabilities, including financials, CRM, e-commerce, and inventory management. Oracle NetSuite’s real-time visibility into business performance and ability to scale with the business make it a preferred choice for dynamic and fast-growing companies.
- Sage Intacct: Specialising in financial management, Sage Intacct is a popular choice for businesses needing robust accounting features. It provides deep financial insights, automation of complex processes, and strong compliance support. Sage Intacct’s integration with other business systems and its focus on financial transparency and control make it an excellent solution for finance-centric organisations.
- Infor CloudSuite: Infor CloudSuite offers industry-specific ERP solutions designed to meet the unique needs of various sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, and retail. Its advanced analytics, user-friendly interface, and strong integration capabilities make it a valuable tool for businesses looking to enhance operational efficiency and decision-making.
- Epicor ERP: Epicor ERP is tailored for manufacturing, distribution, retail, and services industries. It provides end-to-end solutions that help businesses improve performance, productivity, and profitability. Epicor’s strong focus on industry-specific needs and its ability to support complex manufacturing processes make it a standout option for these sectors.
- Acumatica: Acumatica is a cloud-based ERP solution that offers a full suite of integrated business management applications, including financials, distribution, manufacturing, project accounting, and CRM. Its flexible licensing model, comprehensive functionality, and mobile access make it suitable for businesses looking for a scalable and cost-effective ERP solution.
Read more: Compare Top ERP Software on the Market
Conclusion
ERP systems have become essential for UK businesses looking to enhance efficiency, improve decision-making, and stay competitive in a dynamic market. By understanding the basics of ERP, recognizing its benefits, and following best practices for implementation, businesses can unlock new levels of productivity and success.
If you’re considering implementing an ERP system, it’s crucial to choose a solution that aligns with your business needs and to partner with experienced professionals who can guide you through the process.
Ready to transform your business with ERP? Contact us for a free consultation today!
More to Read:
Industries that benefit most from ERP
3 Factors that will Impact Your ERP selection
ERP Comparison Chart Between Dynamics 365: Business Central and Finance & SCM
How Much Does An ERP System Cost?
How Cloud ERP software Can Make Businesses More Agile
This Is Why Your Company Need An ERP Solution Today
The hidden costs of NOT implementing ERP: Why you can’t afford to wait to implement ERP

