Choosing between Dynamics 365 Business Central and Dynamics 365 Finance & Supply Chain Management (F&SCM) becomes more complex when your business handles inventory depth, forecasting models, or manufacturing processes. Each system offers strong capabilities, but the level of control and scalability differs as operations grow.
Part 2 of our Microsoft ERP comparison explores operational differences for organizations evaluating manufacturing ERP software and capabilities of Microsoft Dynamics 365 for manufacturing.
Watch the full Part 2 walkthrough on YouTube:
What Are the Operational Differences Between Dynamics 365 Business Central and Finance & Supply Chain?
In Part 1 of our comparison series, we explored the financial and compliance differences between the two systems, including usability, global consolidation, regulatory controls, and audit capabilities. Those areas form the foundation of how organizations manage their financial health and governance.
You can read Part 1 here: Dynamics 365 Business Central vs Finance & Supply Chain Management (Part 1)
Part 2 shifts the focus to operational functionality, where the real differences appear for companies with inventory, production, or supply chain demands. When evaluating ERP systems from an operational perspective, the distinction becomes clearer in how each platform handles:
- Item tracking and inventory dimensions
- Demand forecasting
- Manufacturing models
- Costing and cost management
These capabilities influence daily execution across procurement, warehouse management, production planning, and cost control. Understanding these operational differences, combined with the financial and compliance insights from Part 1, provides a full picture of how each ERP supports business growth.
Item Tracking Dimensions
Accurate item tracking is essential for manufacturers and distributors managing products with variations in size, color, material, formulation, or batch attributes. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, food and beverage, automotive parts, and consumer goods rely heavily on precise traceability to maintain quality, meet regulatory requirements, and support efficient warehouse operations.
Both Business Central and Finance & Supply Chain Management provide item tracking capabilities, yet the level of depth and control differs significantly. Organizations comparing ERP software for supply chain management often evaluate this area early, since traceability influences planning, compliance, and execution across the supply chain.
Business Central offers practical and straightforward item tracking features designed for small and midsized companies. These Business Central item tracking capabilities support serial numbers, lot numbers, and expiration dates, allowing teams to track where an item originated, when it was received, and how it moves through the organization. Reports such as Inventory Valuation or Item Ledger entries can be filtered by tracking numbers, giving planners and inventory managers clear operational and financial visibility. For companies that need lightweight variant management, Business Central supports item variants, which simplifies tracking for organizations that do not require detailed dimension-based structures.
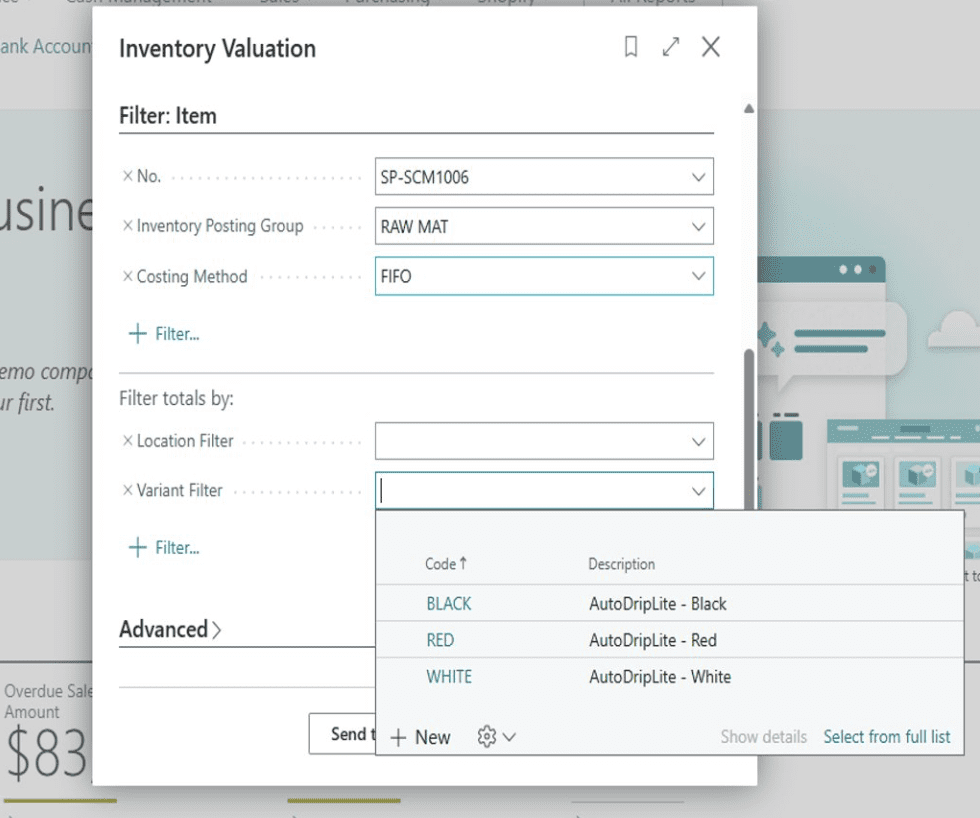
Finance and Supply Chain Management delivers a more advanced and scalable approach through its Inventory Dimension Groups. These dimensions include site, warehouse, location, inventory status, batch, and serial, allowing businesses to track inventory at multiple layers across global or multi-site operations. This granular structure is critical for companies that manage regulated products, high-volume distribution, or complex manufacturing processes.
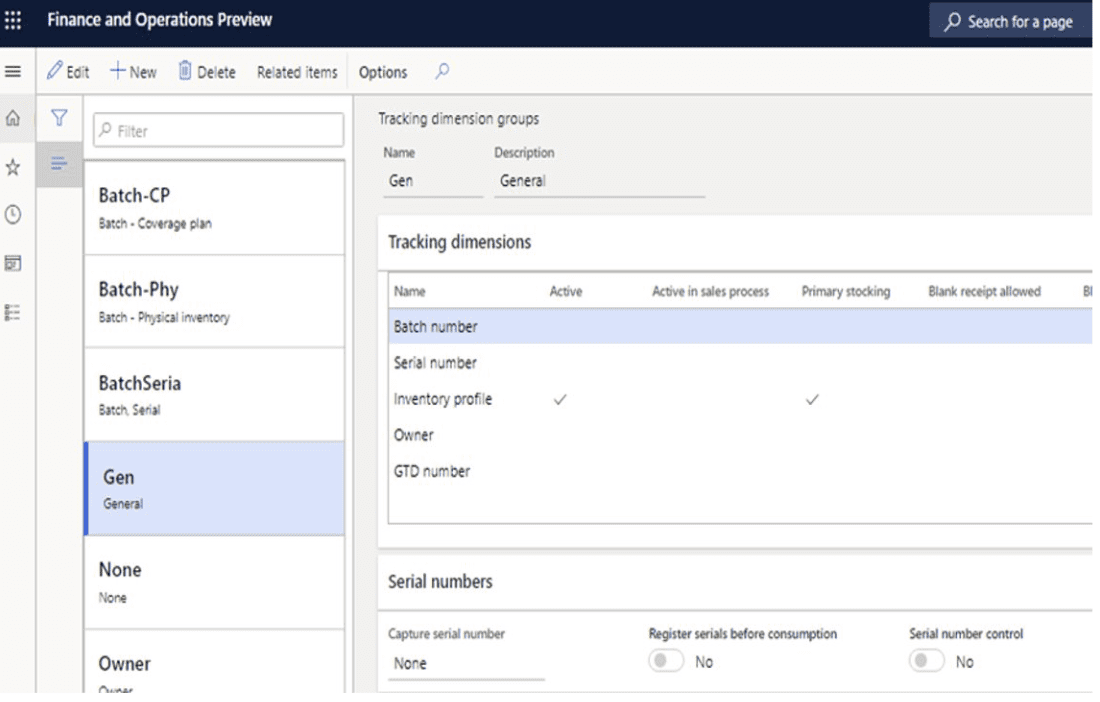
F&SCM also distinguishes between product dimensions and tracking dimensions, an important concept for organizations with large product catalogs. Product dimensions such as size, color, style, and configuration define the commercial and physical characteristics of an item. Tracking dimensions, on the other hand, support the operational flow by identifying where an item is stored, which batch it belongs to, and which specific unit was consumed or sold. This separation gives enterprises full visibility across both product variations and operational tracking requirements.
A key benefit of F&SCM is its ability to automatically generate and manage combinations of product and tracking dimensions, significantly reducing manual effort. Users can define dimension groups and use matrix views to visualize and maintain these combinations, a feature not available in Business Central. This depth is especially valuable for organizations assessing ERP for supply chain management that require multi-site visibility, regulatory traceability, or high-volume warehouse operations.
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is a critical component of inventory planning, production scheduling, and overall supply chain efficiency. Both Business Central and Finance & Supply Chain Management support forecasting, but the depth, flexibility, and automation differ significantly.
Organizations comparing planning tools within the Microsoft ecosystem often evaluate how Dynamics 365 demand forecasting contrasts with the standard Business Central demand forecast experience, especially when forecasting across multiple warehouses, channels, or product families.
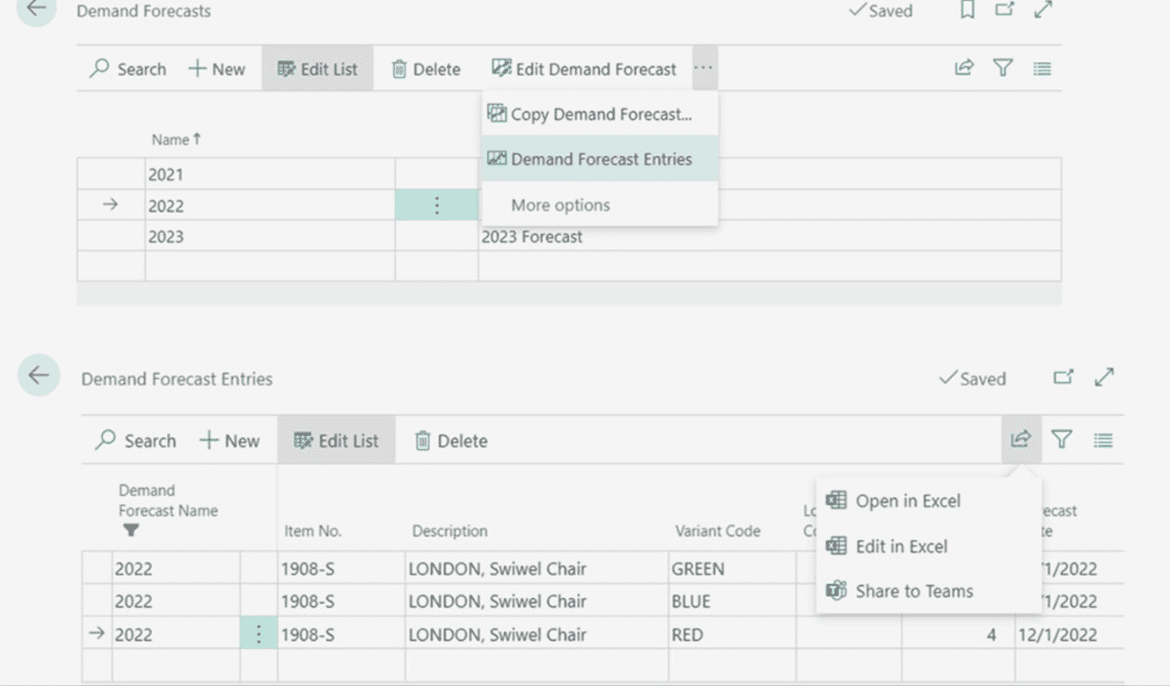
Business Central provides a straightforward approach to item-level forecasting. Users can manually enter sales or production forecasts or import them from Excel, and these values flow directly into the planning worksheet to generate supply orders. Forecasting is typically done by item and by period, such as daily or monthly intervals. While Business Central does not include built-in statistical or AI-driven models, this simplicity works well for companies with stable demand patterns and predictable seasonal cycles. More advanced forecasting can be achieved through extensions such as Power BI, Azure Machine Learning, or third-party applications.
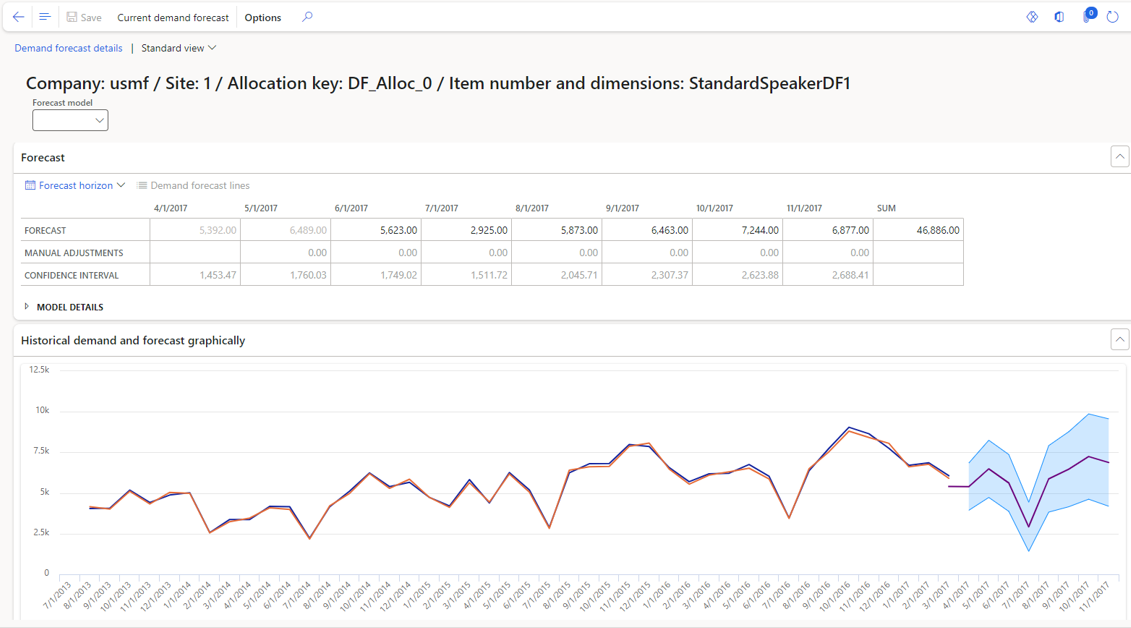
Finance & Supply Chain Management delivers a more advanced and scalable forecasting framework designed for complex operations. Its dedicated forecasting module supports multiple time-series models, segmentation by product or customer, outlier detection, historical trend analysis, and AI-enhanced statistical forecasting through Azure Machine Learning. Forecasts can be generated automatically and are tightly integrated with master planning, allowing organizations to create more accurate production schedules, align procurement activities, and coordinate replenishment across multiple warehouses or global operations.
As operational demands increase, the contrast between the two systems becomes clearer. Business Central is well suited for small to midsized organizations with predictable sales cycles and straightforward planning requirements. Finance & Supply Chain Management, on the other hand, is built for companies that need precision, automation, and scalability in their forecasting processes. Its ability to model complex supply chains makes it the preferred choice for organizations that depend heavily on sophisticated Dynamics 365 demand forecasting capabilities.
In summary, Business Central offers a practical, manual forecasting approach that is easy to use and flexible for smaller businesses. Finance & Supply Chain Management provides an enterprise-ready forecasting solution with advanced analytics, automation, and AI-driven insights for organizations that require higher accuracy and planning depth.
Manufacturing Models and Production Capabilities
Manufacturing is one of the most significant functional differences between Business Central and Finance & Supply Chain Management. Organizations researching Microsoft Dynamics 365 for manufacturing or evaluating modern manufacturing ERP software often begin by comparing how each system supports discrete, process, and lean production environments. While both products offer production capabilities, the breadth, automation, and scalability differ considerably.
Discrete Manufacturing
Discrete manufacturing focuses on assembling products from individual components, and both systems support this model, though at very different levels of depth.
Business Central provides strong foundational tools for discrete manufacturing, including:
- Production orders
- Bills of Materials (BOMs)
- Routing
- Work centers
These capabilities make Business Central a reliable choice for:
- Make-to-stock
- Make-to-order
- Assembly-to-order
- Small batch or light production
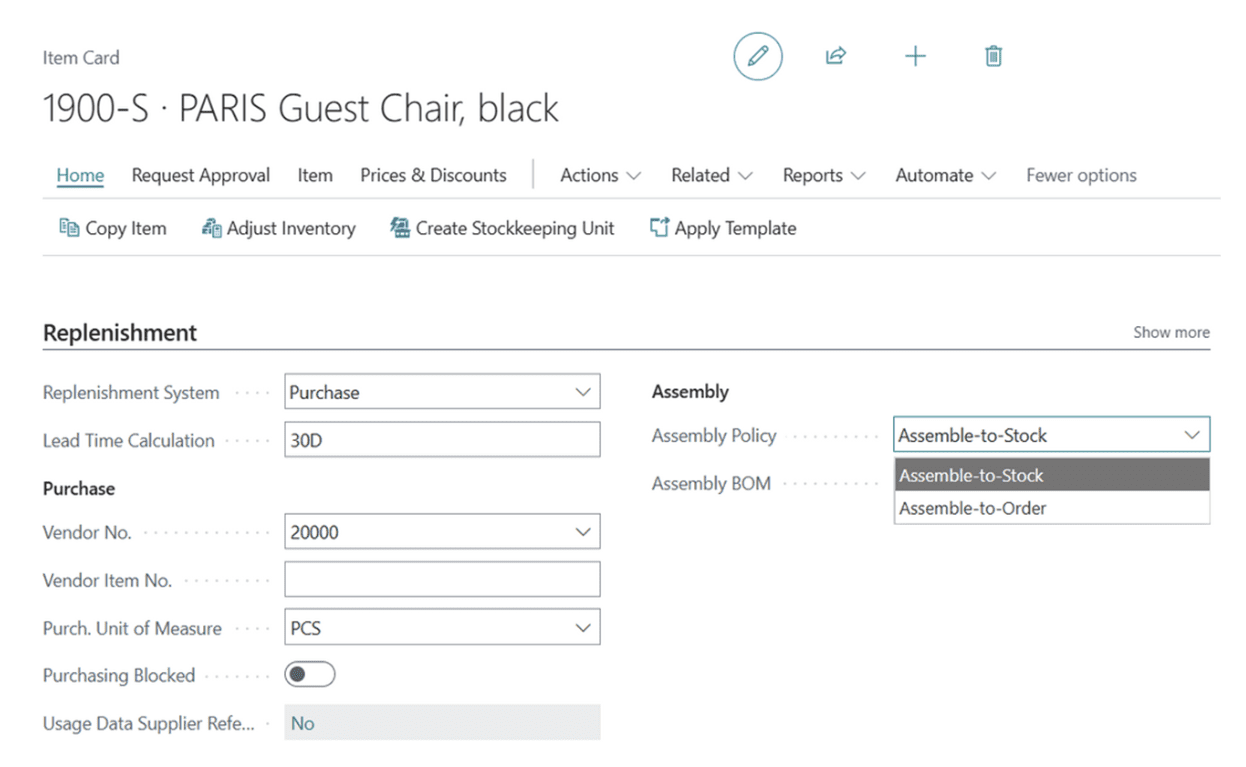
Business Central handles straightforward assembly and routing needs effectively, although it has limitations when supporting complex, multi-level routing or engineering-driven production environments. Because of this, it is often selected by organizations evaluating Dynamics 365 Business Central for manufacturing and looking for core Dynamics 365 Business Central manufacturing capabilities tailored to assembly-focused or light discrete production. For companies evaluating a modern discrete manufacturing ERP, Business Central meets core needs without the overhead of enterprise-level production control.
Case Study: Discrete Manufacturing
Daico Industries (Electronics Manufacturing)
Daico Industries implemented Dynamics 365 Business Central to replace an unsupported legacy ERP system that had limited functionality and constrained operational visibility. As a discrete electronics manufacturer serving defense and aerospace customers, Daico required accurate production time tracking, detailed cost visibility, and stronger reporting to meet Department of Defense and prime contractor requirements. Business Central enabled improved production tracking, more accurate cost reporting, and integrated quality management processes, helping Daico modernize operations while maintaining compliance and transparency. This implementation demonstrates how Business Central can serve as an effective ERP for discrete manufacturing when organizations need reliable production tracking, cost control, and reporting without the complexity of enterprise-scale systems.
Finance & Supply Chain Management provides comprehensive support for discrete manufacturing through advanced tools and automation that go beyond standard Microsoft Dynamics 365 manufacturing functionality. This depth makes F&SCM a strong choice for organizations evaluating Dynamics 365 discrete manufacturing or comparing modern discrete manufacturing ERP systems, especially those that require greater control and scalability across complex production environments.
Key capabilities include:
- Multi-stage routing
- Resource scheduling
- Advanced production control workspaces
- Multi-site and multi-BOM planning
- Engineering change management
- Product configuration
- Subcontracting support
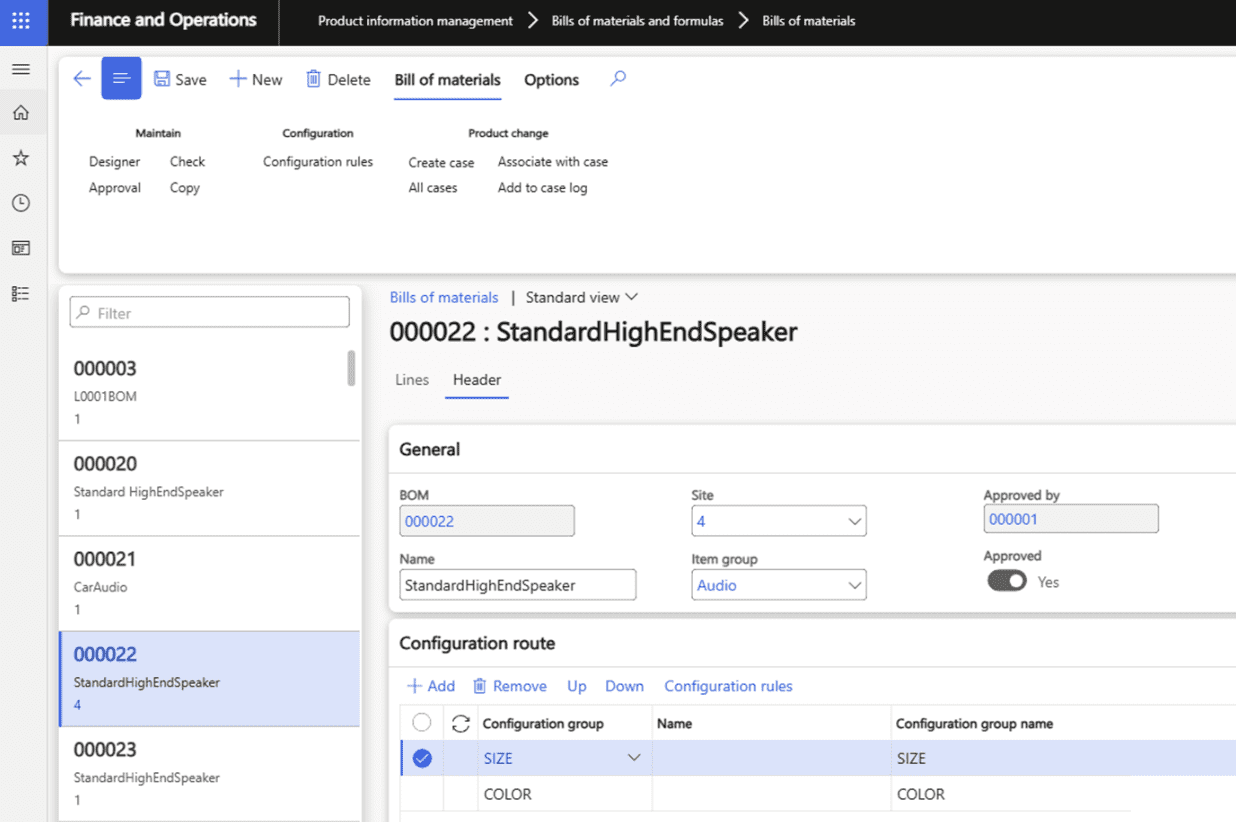
These features are delivered through the Dynamics 365 manufacturing module and enable organizations to manage engineering-driven workflows, high-volume production, and multi-site operations with consistent visibility and precision.
Process Manufacturing
Process manufacturing is common in industries such as chemicals, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and other batch-based production environments.
Business Central has limited native support for true process manufacturing. Many organizations still use it successfully by relying on BOMs and production orders, but it does not include capabilities such as formulas, batch attributes, co-products, or potency management. Companies with more advanced needs often extend Business Central with third-party ISV solutions tailored to process manufacturing ERP requirements.
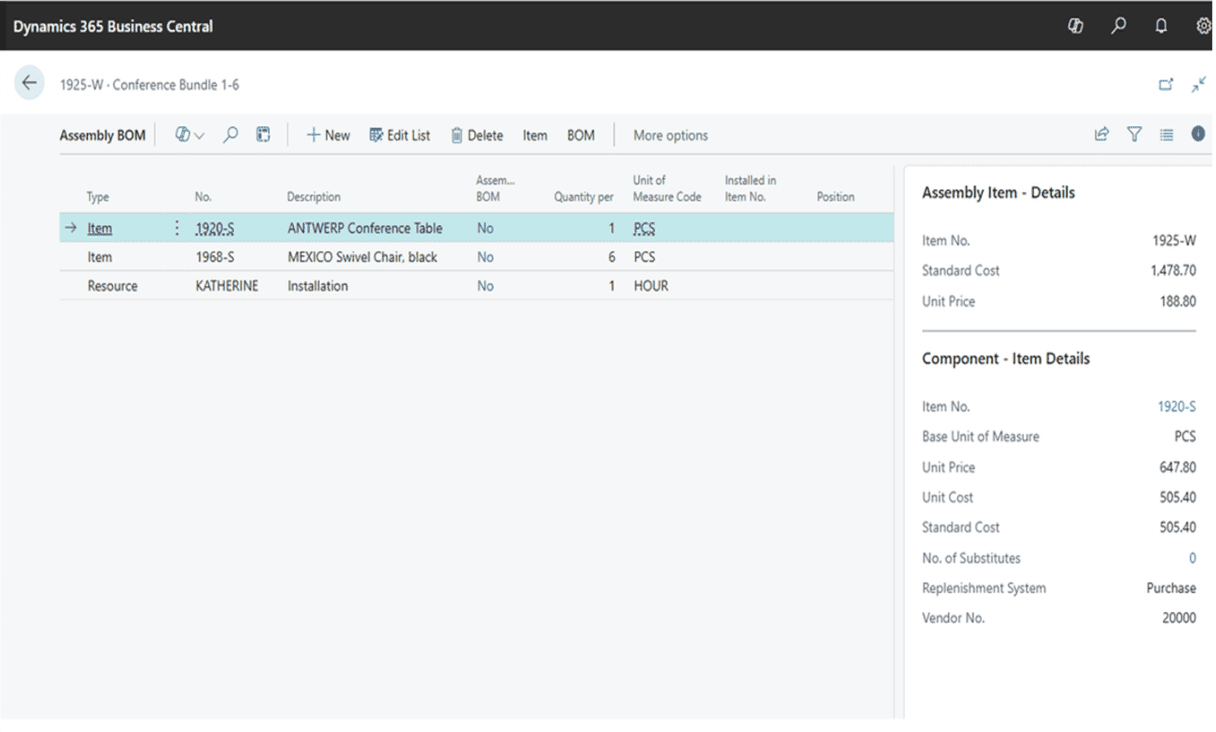
Finance & Supply Chain Management includes full native process manufacturing capabilities, such as:
- Batch orders
- Formulas and recipes
- Co-products and by-products
- Potency and attribute management
- Compliance tracking
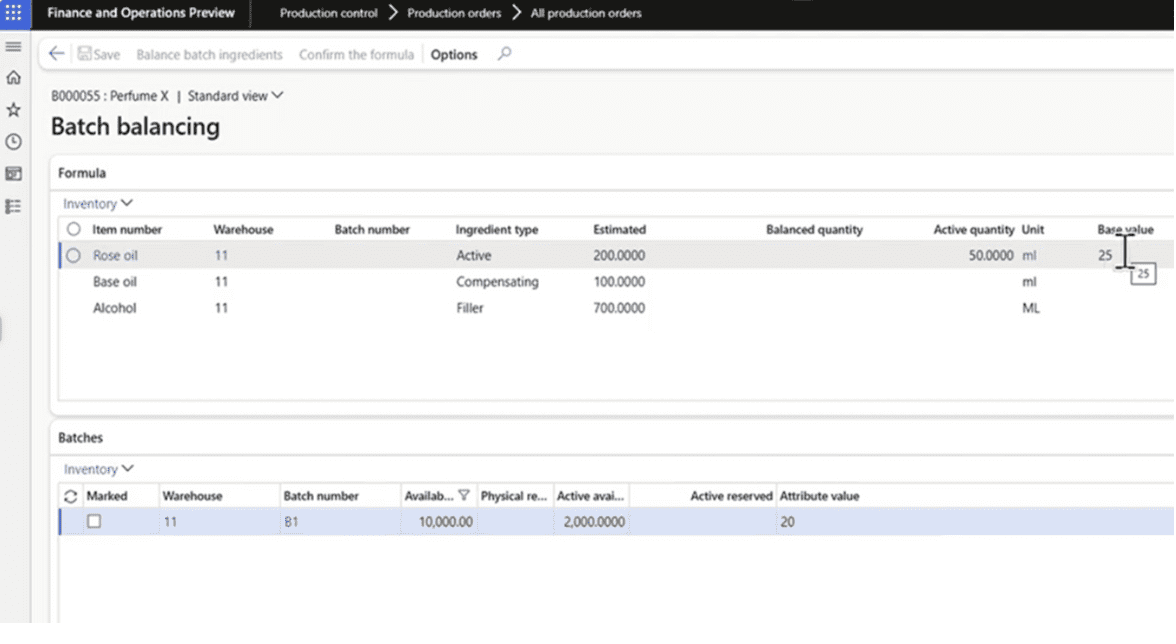
These features make F&SCM a strong fit for highly regulated industries requiring precise batch control, traceability, and complex production structures, and it is frequently chosen by companies replacing outdated process manufacturing software with a modern, scalable ERP platform.
Case Study: Process Manufacturing
MOC Products (Automotive Manufacturing)
An example of process manufacturing in action is MOC Products, an automotive manufacturer that migrated from Ramco ERP to Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations to support continued growth and operational consistency. The implementation unified finance, supply chain management, and manufacturing into a single cloud-based platform, improving inventory accuracy, production planning, and data visibility across operations. This project demonstrates how Dynamics 365 Finance & Supply Chain Management functions as a reliable process manufacturing ERP for organizations with complex manufacturing workflows, multi-module integration needs, and high transaction volumes.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing focuses on reducing waste, improving flow, and increasing efficiency across production operations.
Business Central does not natively support lean manufacturing models. While teams can mimic basic lean principles using assembly orders, custom workflows, or simplified processes, the platform does not include dedicated lean tools for Kanban workflows or event-based scheduling.
Finance & Supply Chain Management provides full lean manufacturing support with:
- Kanban rules
- Production flows
- Pull-based replenishment
- Lean work cells
- Event-driven scheduling
F&SCM’s flexibility allows manufacturers to run lean, process, and discrete production models simultaneously, making it a strong option for companies evaluating Dynamics 365 lean manufacturing or requiring mixed-mode manufacturing across multiple plants or production lines.
If your manufacturing operations are becoming more complex, the ERP choice matters.
Whether you need lightweight discrete manufacturing or advanced multi-site production control, choosing the right Dynamics 365 platform early can prevent costly rework later.
Comparison of Manufacturing Capabilities in Business Central vs Finance & Supply Chain Management
| Manufacturing Area | Dynamics 365 Business Central | Dynamics 365 Finance & Supply Chain Management | What This Means for Your Operations |
| Manufacturing Types Supported | Discrete | Discrete, Process, Lean | FSCM supports more advanced production environments and regulated industries. |
| BOM Structure | Standard BOM for assemblies and production | Multi-level BOM, formula management, co-products, by-products | FSCM handles complex recipes, formulations, and multi-stage production. |
| Routing & Work Centers | Basic routing with work centers and machine centers | Advanced routing, resource scheduling, capacity planning | FSCM is better suited for multi-site production and detailed scheduling needs. |
| Process Manufacturing | Not supported natively | Fully supported with batch orders, potency, attributes, and formula-based production | Ideal for food, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries. |
| Lean Manufacturing | Not supported natively | Supported through Kanban rules, pull-based replenishment, and lean work cells | FSCM enables mixed-mode production combining discrete + lean. |
| Production Control | Standard production orders with limited automation | Deep production control with workspaces, costing versions, and advanced execution tracking | Increased visibility and governance for complex operations. |
| Regulatory/Compliance Fit | Light manufacturing with basic traceability | Suited for regulated industries requiring batch control and full genealogy | FSCM reduces operational risk for companies with strict compliance requirements. |
| Scalability | Best for small to midsized manufacturers | Designed for multi-company, multi-site, global manufacturing operations | FSCM scales with enterprise growth and complex supply chains. |
Summary: Which System Fits Your Manufacturing Needs?
Business Central is best suited for small to midsized manufacturers with straightforward discrete production needs, offering practical tools for assembly and light make-to-order workflows. Finance & Supply Chain Management delivers the depth required for advanced, multi-style manufacturing environments, including discrete, process, and lean scenarios. While many food and beverage companies successfully use Business Central for basic production, organizations with complex, regulated, or multi-site operations typically benefit from the broader capabilities of F&SCM.
Cost Comparison: Business Central vs Finance & Supply Chain Management
Cost is often one of the most influential factors when choosing between Business Central and Finance & Supply Chain Management. While features and capabilities shape long-term value, understanding licensing requirements, implementation costs, and scalability expectations is critical for decision makers evaluating an ERP strategy.
Business Central remains one of the most cost-effective Microsoft ERP options for small and midsized organizations. Licensing typically ranges from 80 to 110 USD per user per month, and companies can begin with a minimum of one licensed user. This flexible entry point allows growing businesses to adopt modern ERP capabilities without a heavy upfront investment. Implementation costs generally fall between 25,000 and 500,000 USD, depending on the scope, integrations, and required customizations.
The platform delivers strong functionality across financial management, inventory, sales, supply chain, and light manufacturing. It integrates with Microsoft 365, Power Platform, and many third-party applications, allowing organizations to automate processes and gain better insight without complex development. For teams seeking agility, controlled budgets, and a predictable path to growth, Business Central offers a scalable and practical solution.
Finance and Supply Chain Management, by comparison, is designed for large organizations operating across multiple entities, regions, or complex supply chain environments. Licensing begins at 210 USD per user per month and can exceed 240 USD, reflecting its advanced capabilities. Unlike Business Central, the system requires a minimum of 20 licensed users, which aligns with its enterprise-level positioning. Implementation costs range from 250,000 USD to more than 1 million USD, particularly for global deployments that involve multi-entity financials, advanced manufacturing, or regulatory requirements.
This investment provides access to a broader set of capabilities, including advanced financials, discrete and process manufacturing, warehousing, procurement, global tax management, compliance controls, and high-volume transaction processing. Finance and Supply Chain Management is frequently compared with enterprise ERP platforms such as SAP and Oracle because of its depth, automation, and scalability across departments and geographies.
When evaluating the cost of an ERP system, the distinction between these platforms becomes clear. Business Central is ideal for organizations that prioritize affordability, ease of use, and fast adoption. Finance and Supply Chain Management is suited for enterprises that require advanced operational control, long-term scalability, and global capabilities. Understanding how both licensing and implementation costs align with your business structure ensures a more informed and successful ERP selection.
Which System Fits Your Operational Requirements?
Choose Business Central if your operations:
- Include standard or light manufacturing
- Have straightforward item tracking needs
- Rely on simple forecasting
- Require low overhead and fast deployment
- Operate regionally or with minimal warehouse complexity
Choose Finance & Supply Chain Management if your operations:
- Require multi-site or multi-warehouse visibility
- Need process or lean manufacturing
- Depend on advanced forecasting and planning
- Have complex costing structures
- Support regulated or global supply chains
Conclusion
Part 2 of this comparison highlights the operational differences that matter most when selecting a manufacturing ERP, including item tracking, demand forecasting, production models, and cost considerations. While both platforms are part of the Microsoft Dynamics 365 ecosystem, they serve different stages of manufacturing and supply chain maturity.
Dynamics 365 Business Central for manufacturing is well suited for small to midsized organizations that need a practical and cost-effective ERP for discrete manufacturing, straightforward forecasting, and basic supply chain management. Its ease of use and flexibility make it a strong option for companies transitioning from spreadsheets or entry-level systems into a structured manufacturing ERP environment.
Finance & Supply Chain Management, on the other hand, is designed for enterprises that require deeper operational control. With advanced capabilities across discrete, process, and lean manufacturing, robust Dynamics 365 production control, AI-driven Dynamics 365 demand forecasting, and multi-site inventory management, it supports complex, regulated, and global operations that depend on precision and scalability.
Organizations evaluating Microsoft Dynamics 365 for manufacturing, comparing ERP for manufacturing, or ERP software for supply chain management should align their choice with production complexity, regulatory requirements, and long-term growth plans. In many cases, Business Central provides everything a growing manufacturer needs. As operational demands increase, Finance & Supply Chain Management becomes the strategic platform for scale, automation, and enterprise-wide visibility.
Not sure which Dynamics 365 ERP fits your manufacturing operations?
Get expert guidance on choosing between Business Central and Finance & Supply Chain Management based on your production complexity, supply chain needs, and growth plans.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Dynamics 365 Business Central is designed for small to midsized manufacturers with straightforward discrete production needs, while Finance & Supply Chain Management supports complex manufacturing environments that require advanced production control, multi-site operations, and multiple manufacturing models. Both are part of Microsoft Dynamics 365 for manufacturing, but they serve different levels of operational complexity.
Yes. Dynamics 365 Business Central for manufacturing is well suited for discrete manufacturing scenarios such as make-to-order, make-to-stock, and assembly-to-order. It provides core manufacturing capabilities including production orders, bills of materials, routing, and item tracking, making it a practical manufacturing ERP for growing organizations.
Finance & Supply Chain Management supports discrete, process, and lean manufacturing natively. This includes advanced capabilities for batch production, formulas, Kanban workflows, and mixed-mode manufacturing, making it suitable for organizations that require a full-featured manufacturing ERP software platform.
Manufacturers should consider Finance & Supply Chain Management when operations require advanced production control, multi-site manufacturing, process or lean manufacturing, regulatory traceability, or high-volume transaction processing. These scenarios often exceed the core Dynamics 365 Business Central manufacturing capabilities.
Business Central can be extended using third-party solutions, Power Platform tools, and integrations to support more advanced manufacturing requirements. However, organizations with long-term needs for process manufacturing or lean manufacturing often find Finance & Supply Chain Management to be a better strategic fit.

